Cancer Treatment Options
Cancer Treatment Options
Proton Therapy

What is proton therapy
1. What is proton therapy?
A proton is a particle of hydrogen that has a positive charge after losing its electron.
Proton therapy is one of the most advanced radiotherapy techniques in the world.
2. Characteristics of proton therapy
Proton therapy is a non-invasive, high-precision radiotherapy method. In traditional radiotherapy, X-rays will cause great damage around tumor tissues after entering the body, while protons have a unique physical property called Bragg peak. Before arriving at the tumor, protons emit very little energy and hardly damage normal tissues. After entering the tumor tissue, the energy is rapidly released and directional blasting, and after penetrating the tumor tissue, the energy is sharply attenuated, so that the surrounding normal tissue is not damaged.
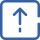
Proton therapy equipment
The Proton Therapy Center was set up in Hebei Yizhou Cancer Hospital and introduced Belgium IBA Proteus PLUS proton therapy system, equipped with advanced CBCT image guidance system, respiratory gated technology, pen beam scanning technology and 360° rotating rack. The proton accelerator consists of five treatment modules, including four rotating rack treatment rooms and one fixed beam treatment module; With 4 pen beam scanning treatment heads and 1 universal treatment head (with two functions of double scattering and pen beam scanning), it is one of the largest proton therapy centers in the world with advanced technology, complete functions and large scale.
Indications
- Cranial base chordoma
- pancreatic cancer
- lung cancer
- Medulloblastoma
- renal cell carcinoma
- liver cancer
Head and neck tumors: eye tumors, craniopharyngioma, skull base chordoma, skull base chondrosarcoma, nasopharyngeal cancer, nasal and sinus malignant tumor, parotid gland malignant tumor, oropharyngeal cancer, oral malignant tumor, adenoid cystic cancer, tongue base cancer, throat cancer, recurrent head and neck malignant tumor;
Chest tumors: lung cancer, esophageal cancer, thymoma, malignant pleural mesothelioma, lung metastases, breast cancer;
Abdominal tumor: abdominal wall tumor, gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, small intestine tumor, liver cancer, bile tumor, pancreas tumor, spleen tumor, peritoneal and retroperitoneal tumor, gastrointestinal and pancreatic neuroendocrine system tumor;
Pelvic cancer: kidney cancer, rectal cancer, anal canal cancer, prostate cancer, bladder cancer, endometrial cancer, cervical cancer, vaginal cancer;
Central nervous system tumors: meningioma, glioma, pituitary tumor, medulloblastoma, ependymoma, intracranial germinoma, primary central nervous system lymphoma, spinal cord tumor;
Bone and soft tissue tumors: leiomyosarcoma, epithelioid sarcoma, Ewing's sarcoma, osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, boat tail chordoma, giant cell tumor of bone, hemangioperytoma, hemangioendothelioma;
Skin tumors: malignant melanoma, skin squamous cell carcinoma;
Hemolymph system tumors: Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma;
Childhood tumors.
Therapeutic advantages
-
The radiation dose of tumor target area was increased, and the tumor control rate was improved
-

Reducing energy irradiation in non lesion areas reduces damage to normal tissues and organs in the human body, and reduces radiation related side effects
-

Proton therapy can effectively protect children's physiological functions, reduce the impact on their physical development and intelligence
-

Improve quality of life, improve local tumor control rate and survival rate
-

Reduce the risk of secondary tumors
-

Provided new treatment methods for patients who cannot undergo surgery
-

Providing an opportunity for secondary radiation therapy for patients who have relapsed after traditional radiation therapy in the past
Proton Therapy Process

Step 1: Make an appointment for registration. Patients can make appointments and register through official phone numbers or official WeChat, or go to the outpatient clinic for registration.
Step 2: Visit method: 1. Offline outpatient service. 2. Remote consultation.
Step 3: Inpatient registration
Step 4: Inpatient examination
Step 5: Determine the plan. Each patient in our hospital will arrange MDT multidisciplinary consultations.
Step 6: Preparation for Treatment
Step 7: Proton therapy
Step 8: Handling discharge procedures
Proton Therapy Cases
Proton Therapy FAQ
-
What is proton therapy?
Proton therapy is a relatively advanced tumor radiotherapy treatment technology in the world today. There is a killer trick in proton therapy called the Bragg Peak. After being accelerated by an accelerator, protons enter the human body at extremely high speeds, releasing very little energy along the way. When they reach the tumor, the highest energy is instantly released, forming the Bragg Peak. After penetrating the tumor, the radiation dose drops sharply, even to zero. Proton radiation can perform precise cutting like a surgical knife at the edge of a tumor, just like carving flowers on tofu, without causing surgical wounds. For patients, radiation therapy has become a non-invasive treatment method. Most patients only need to lie on the treatment bed for a few minutes at a time, and after taking the radiation, they can go home. Many patients do not need to be hospitalized.【Open】 -
Can children receive proton therapy?
Proton therapy is very suitable for children. From an age perspective, proton therapy is very suitable for children, almost suitable for all age groups. If pediatric cancer patients meet the requirements of proton therapy, they may have an 85% chance of achieving clinical cure. Because proton radiotherapy has the advantages of high precision, targeted "explosion", and minimal damage to normal cells, it causes minimal damage to the surrounding normal tissues of the lesion. This therapy has fewer side effects and a lower recurrence rate for children's longer growth process, and is more beneficial for pediatric cancer patients. Children are more sensitive to radiation, and their long-term life and quality of life are very important. Of course, if they can eat less radiation, they choose not to. Especially for children with brain tumors, if they meet the indications, the use of this treatment method can greatly reduce the accumulation of radiation during radiotherapy, effectively control the radiation dose in key areas of the child's brain, and be beneficial to the health of the child's tissues.【Open】 -
How long does proton therapy take?
The process of proton emission to the tumor takes 1 minute, and the entire treatment process takes about 3 minutes. Adjusting the appropriate posture takes about 25 minutes, so the time required for a single treatment is about 30 minutes. After treatment, patients can leave the treatment center and engage in normal daily activities. The length of the treatment cycle depends on the tumor itself and its location. Generally, treatment is required 5 days per week for 4-6 weeks.【Open】 -
Can proton therapy be used for metastatic lung cancer?
In the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, whether the lesion has metastasis is an important factor affecting prognosis. When metastatic cancer lesions are discovered, there must also be microscopic lesions, which cannot be confirmed through imaging examination. Therefore, this situation is usually not suitable for local therapy. However, there is a very special type of metastasis, which can still be treated with surgery or radiotherapy, even though distant metastasis has already occurred. It is called "oligometastasis". 1. The applicable standards for proton therapy for metastatic lung cancer do not limit the type of primary cancer, but require that there be no more than 3 metastatic lesions, including the primary lesion, without any other obvious lesions (the primary lesion has already been treated). 2. Compared with targeted X-ray irradiation, proton therapy has the advantage of reducing the radiation range to the lungs and reducing the risk of lung dysfunction. Therefore, it can also be applied in cases of low lung function and multiple metastases. In addition, proton therapy has good therapeutic effects on lung metastases from radiation resistant tumors such as colorectal cancer, kidney cancer, and thyroid cancer.【Open】 -
Can liver cancer be treated with proton therapy?
The preferred treatment for primary liver cancer is surgery, but most patients are already in the middle and late stages of treatment, losing the opportunity for surgery. For patients who cannot undergo surgical resection or are unwilling to undergo invasive treatment, radiation therapy has become a new option. Some liver cancer patients who cannot be surgically removed may have their tumors shrink or decline after receiving radiation therapy, which can be converted to surgical resection. Postoperative adjuvant radiation therapy can also reduce local recurrence or distant metastasis of lesions and prolong the tumor free survival of patients. Radiation therapy for liver cancer has been abandoned due to the limitations of traditional radiation therapy techniques, mainly because the normal liver tolerance dose (30Gy for the whole liver) is much lower than the tumor lethal dose (50-70Gy). Not only is the tumor dose insufficient, but it can also lead to radiation hepatitis, causing short-term death of patients with high risk and poor efficacy. Unlike traditional radiotherapy, proton therapy can concentrate more radiation dose on the lesion site, resulting in a more significant therapeutic effect. At the same time, proton therapy causes less radiation damage to surrounding normal liver tissue and tissues along the path of radiation entering the human body. It also has less radiation dose on the kidneys, stomach, intestines, and heart, effectively reducing the toxic side effects of radiotherapy on the human body.【Open】
Related Reading
-
Proton therapy is a "cancer weapon"? Significant advantages in treating pediatric chordoma, with a 5-year survival rate of 91%
The actual results showed that the 5-year local control rate was 92%, the 5-year progression free survival rate was 92%, and the overall 5-year survival rate was as high as 91%.
2023-08-24 -
Most complete! A detailed explanation of proton therapy for pediatric tumors!
Proton therapy, as an advanced technology for treating childhood tumors, has gained increasing recognition. Prioritizing proton therapy for children is of great significance in improving their future quality of life.
2023-08-22 -

Indications and clinical effects of proton therapy, once explained
Many friends leave messages asking: What cancers can proton therapy treat? What is the clinical effect of proton therapy? Below, we will summarize the indications and clinical results of proton therapy together.
2023-08-22 -

Why do many internationally renowned surgeons recommend proton therapy for patients with brain tumors?
Proton therapy can avoid or reduce the radiation dose to normal tissues around tumors, thereby avoiding or reducing the occurrence of early and late adverse reactions in normal tissues.
2023-08-22 -
Got an eye tumor, can only the eyeball be removed? Proton therapy has an eye protection rate of up to 90% and a 10-year survival rate of 93%!
The prognosis of proton therapy for ocular tumors is good, with over 98% of patients experiencing disappearance or permanent cessation of tumor growth, and over 90% of patients retaining their eyes.
2023-08-22